ECG
Electrocardiogram Test
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG), recording and, a graph of voltage for the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect a small electrical change in cardiac cycle that are caused by the depolarization of cardiac muscle followed by repolarization. Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction), and electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia and hyperkalemia).
In a conventional 12-lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient’s limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart’s electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (“leads”) and is recorded over a period of time (usually ten seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart’s electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle.
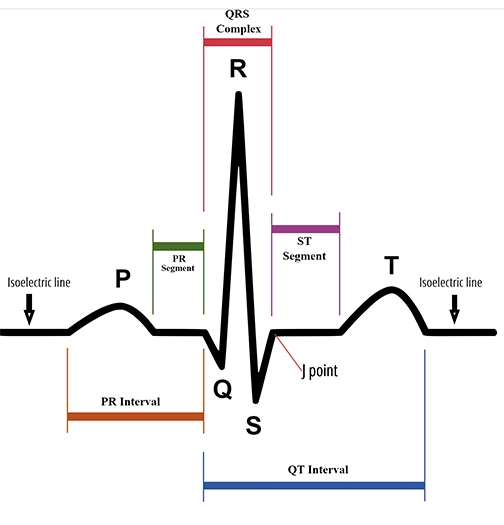
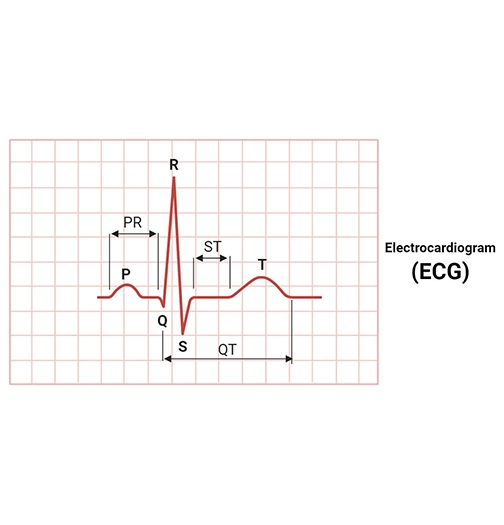
There are three main components of ECG: the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents the depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave, which represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
ECG Procedure
During ECG, patients are made to lie flat on a table and about 10 small sticky sensors called electrodes will be attached to your arms, legs and chest. These are connected by wires to an ECG recording machine. Before attaching the electrodes, you will usually need to remove your upper clothing. While you lay flat, the computer machine records the signal activity in the form of wavy lines on a piece of paper.

An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on the skin. It is a valuable tool for diagnosing heart conditions by measuring the rate and regularity of heartbeats, as well as the size and position of the heart chambers.
features of ECG Test
An ECG test records the electrical activity of the heart to help diagnose heart conditions. It shows the heart rate, rhythm, and various wave patterns that can indicate problems like arrhythmias, heart attacks, or conduction abnormalities. ECGs are non-invasive and provide valuable information about the heart’s health and function.
FAQ
How long does an ECG test take?
An ECG test typically takes only few minutes to perform. However, if additional monitoring is required, such as a 24-hour Holter monitor, the test may last longer.
What does an ECG test diagnose?
An ECG test helps diagnose a wide range of heart conditions, including heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias), heart attacks, coronary artery disease, heart valve problems, and congenital heart defects.
Is an ECG test safe?
Yes, an ECG test is considered safe and non-invasive. It does not involve radiation exposure, and there are no known risks associated with the procedure.
Who interprets the results of an ECG test?
A cardiologist interprets the results of an ECG test. They analyze the ECG tracings to diagnose heart conditions and determine appropriate treatment plans.
Will I feel any discomfort during an ECG test?
No, an ECG test is painless and generally well-tolerated by patients. You may feel a slight discomfort when the electrodes are removed from your skin, but it should not cause any lasting discomfort.
What Facilities We Provided

Eye Care Services

Cardiology Services

