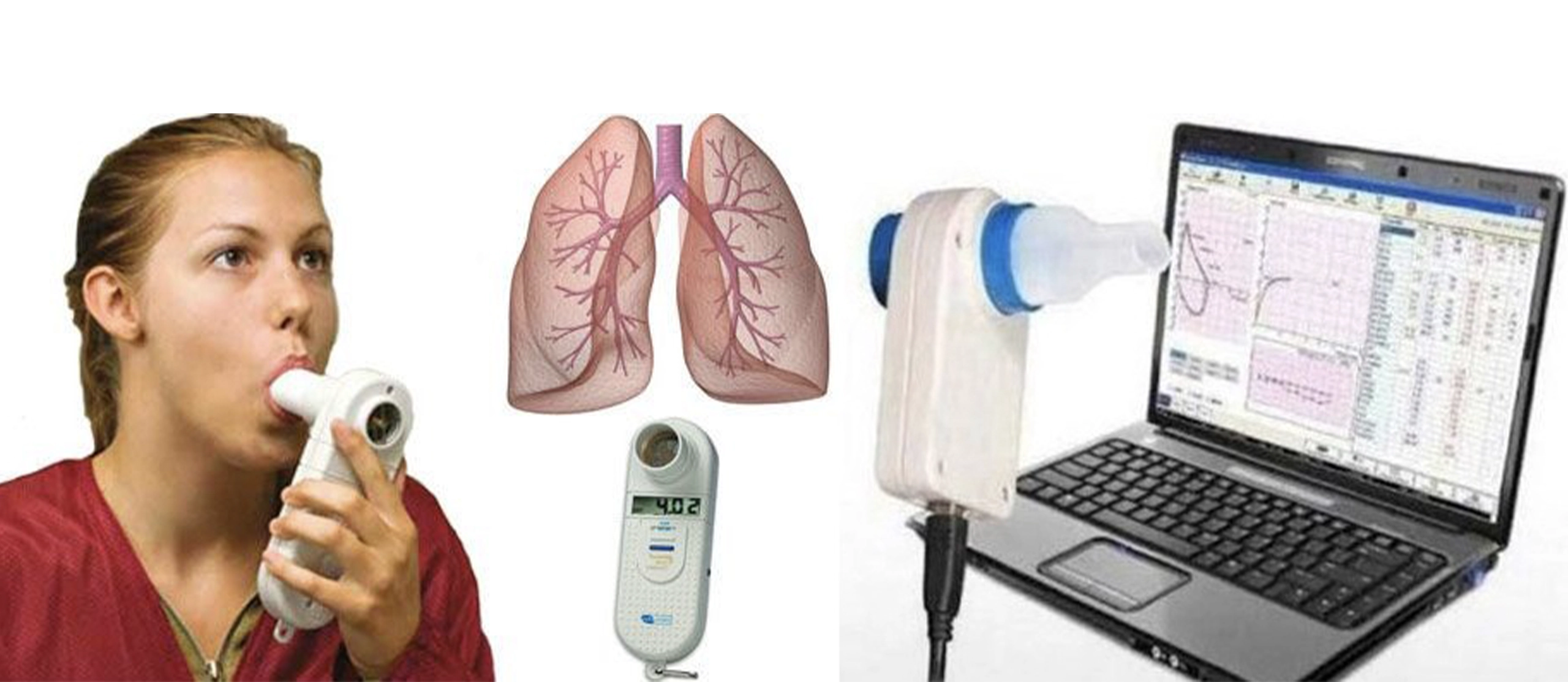
In the realm of respiratory health, the pulmonary function test (PFT) stands as a cornerstone diagnostic tool. It offers valuable insights into the functionality of the lungs, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various respiratory conditions. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the pulmonary function test, unraveling its significance and how it contributes to maintaining optimal lung health.
Understanding Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
At its core, a PFT assesses how well your lungs are working by measuring key parameters such as lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange. These tests are non-invasive and typically involve breathing maneuvers into specialized equipment under the guidance of a trained healthcare professional.
Types of Pulmonary Function Tests
- Spirometry: This is one of the most common PFTs. It measures the amount (volume) and speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is crucial in diagnosing conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung diseases.
- Lung Volume Measurement: This test quantifies the amount of air present in the lungs after a maximal inhalation (total lung capacity) or after a normal exhalation (functional residual capacity). It helps in differentiating between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
- Diffusion Capacity Test: Also known as the DLCO test, it evaluates how well oxygen moves from the lungs into the bloodstream. This is essential in diagnosing conditions affecting the gas exchange process, such as pulmonary fibrosis or emphysema.
Importance of Pulmonary Function Tests
- Diagnosis: PFTs play a pivotal role in diagnosing various respiratory disorders, helping healthcare providers formulate appropriate treatment plans tailored to individual patients.
- Monitoring: For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD, regular PFTs help track disease progression and treatment efficacy, enabling timely adjustments to management strategies.
- Preoperative Evaluation: PFTs are often conducted before surgery to assess lung function and identify potential risks associated with anesthesia and surgery, ensuring safer outcomes for patients.
Preparing for a Pulmonary Function Test
Before undergoing a PFT, it’s essential to follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider. This may include avoiding certain medications, refraining from smoking, and wearing comfortable clothing.
During the test, you’ll be instructed to perform various breathing maneuvers, such as deep inhalations and forceful exhalations, while connected to the PFT equipment. The process is painless and typically takes around 30 to 60 minutes to complete.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pulmonary function test serves as a cornerstone in the assessment of lung health, offering valuable insights into respiratory function and aiding in the diagnosis and management of a wide range of respiratory conditions. By understanding the significance of PFTs and their role in maintaining optimal lung health, individuals can take proactive steps towards preserving their respiratory well-being.